Good Companies Do Not Stand Against the Tide of Change
Published Oct 07, 2019 by Susan Moore
Workforce development partnerships, programs, and initiatives were in the spotlight as a delegation of Harvard University professors and administrators visited Houston to explore real-world examples of effective mechanisms, partnerships, and programs to address skills gaps that are driving real results.
The group met with prominent area businesses, educational institutions, and community-based organizations to learn about programs that offer students quality work-based-learning opportunities and direct pathways into meaningful careers and how academic programs are aligned to meet industry standards and needs.
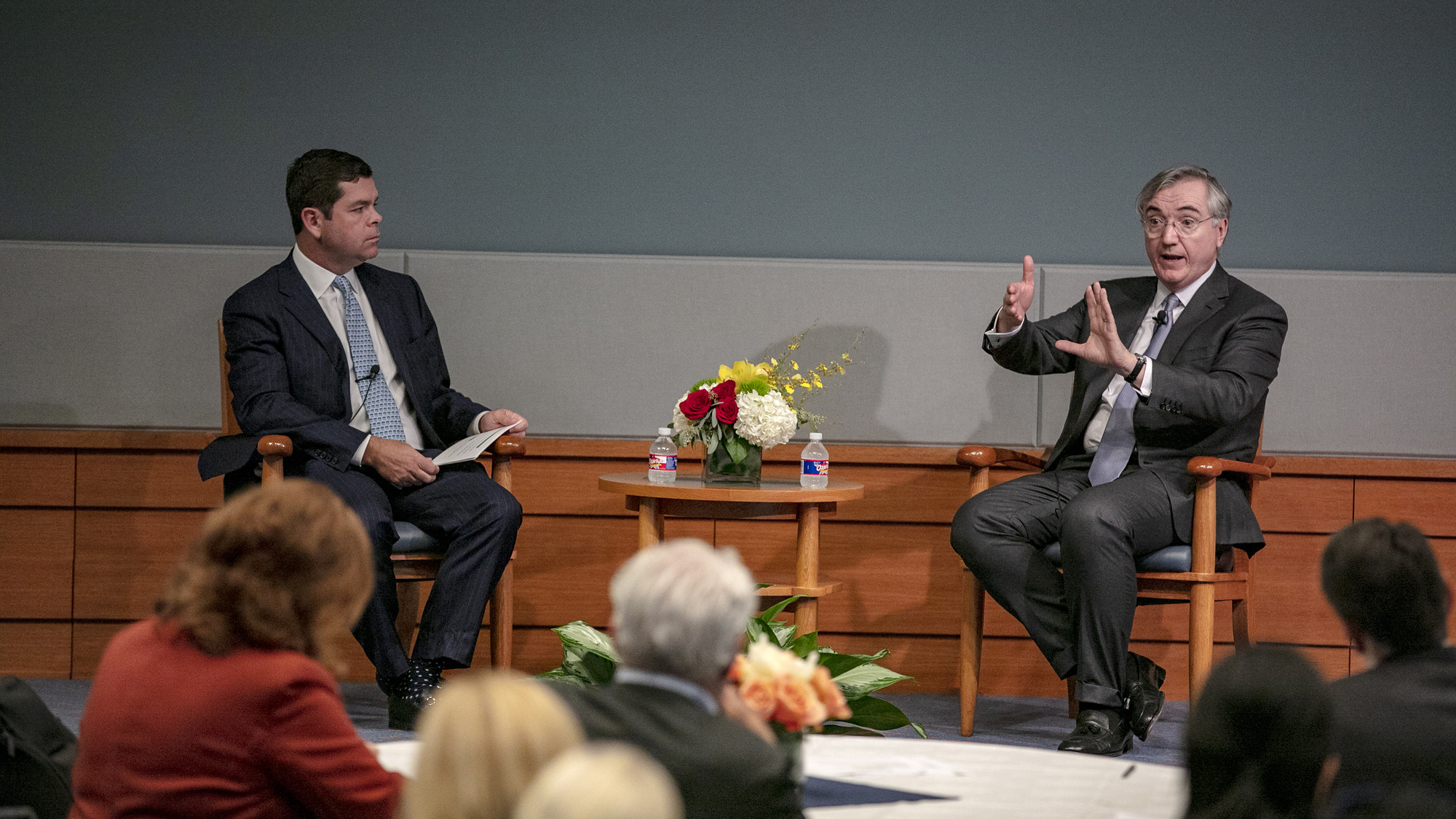
While in town, Harvard Business School professor Joseph Fuller addressed the Greater Houston Partnership’s UpSkill Houston’s Executive Committee and numerous stakeholders at the committee’s October meeting and a forum held at the Federal Reserve Bank of Dallas – Houston Branch.
Fuller, who was the founder and long-time CEO of the consulting company, Monitor, now Monitor-Deloitte, co-leads Harvard’s Managing the Future of Work project, which pursues research that business and policy leaders can put into action in order to navigate a complex workforce landscape.
Fuller focused his comments in Houston on his research and how companies, in Houston and beyond, can respond to strengthen their workforce.
Here are five takeaways from the discussion:
Good companies embrace change
Historically, the approach to finding labor was stable: through want ads in the newspaper. In 1941, only 4 percent of adult males went to college. By 1969, that number had only grown to 10 percent.
The rate of technological change, globalization, and other forces have led to a gradual but accelerating shift in the demand for skills to need people with advanced social skills and technical skills.
Traditional want ads have been replaced by online job boards, head-hunters seek talent through networks such as LinkedIn, and various jobs can be done in other countries. But the processes by which companies manage have not caught up to the pace of change, and it’s time companies revisit those processes.
“Good companies are ones that don’t stand against the tide of those types of changes,” Fuller said. "They embrace them, and, ideally, hope to create their response as a form of competitive edge.”
Employer hiring practices exacerbate the known skills gap for jobs that traditionally did not require a college degree for entry
So-called ‘hybridization’ of jobs, for example, through the incorporation of technology and automation into tasks that previously could be done manually, has led to a new level of complexity and new rate of change in those roles. The requirements for this type of work started accelerating but traditional K-12 education programs have not kept pace, leaving graduates without the proper skills to fill these jobs. Meanwhile, employers have recognized the new scope of skills their workers need, and many have responded by raising educational requirements for job applicants thinking it is the only way to find workers with those skills. The phenomenon of requiring a higher degree for a job than is truly necessary is called ‘degree inflation,’ and it is important to acknowledge that a degree also doesn’t reflect that mastery of skills needed in the workplace.
Across the country, the ratio of jobs that require a college degree is roughly two to three times higher than the size of the population that holds a college degree, he said, adding that requiring a college degree excludes significant proportions of certain ethnic populations from the potential pool of otherwise qualified applicants.
Vocational education has been effectively marginalized through program defunding and a cultural belief that success requires a four-year college degree.
Integrated work-based-learning is a must
The old model of graduating from school, be it high school or a college program, and then starting at a job is a “very, very wasteful system,” Fuller said.
Global data show that the key to having a successful 26-year-old is to get a 16-year-old interested in a career and interested in how they’re going to obtain it and economic independence.
This can be accomplished by building workplace experience into education programs and paying students for their work. Exposing young people to work and work environments in this way sends affirmative messages that they can learn and they can earn, and it makes the transition from a school setting to a work setting feel safer, especially in a setting where an employee needs to demonstrate soft skills, or foundational skills, on the job.
“If you (as employers) are saying we increase supply of qualified, middle-skills job candidates in our city and you don’t have work-based-learning opportunities, paid work-based-learning opportunities, you’re not regularly meeting with a school district, you have not engaged local community college, you do not have a strategy,” Fuller said.
Improve access to workforce, education, and career information
Most students enter college with the aim of getting a good job but many must guess which courses will send them down the path toward that job. Historically, labor market data showing job demand weren’t available. Education providers can now gather data on the types of jobs that are growing and shrinking in a given industry. These data can help inform program design. And by providing degree completion rates and graduate employment rates to incoming students and students deciding whether to enroll in a particular program, educators can help students make informed decisions about their educational and career pathways.
Houston serves as a model for other parts of the country
UpSkill Houston has built a strong foundation for driving change in employer behaviors and educational programs. The right elements are in place, Fuller said. Employers, educators, public entities, and community-serving organizations are at the table, using data, and being realistic about transportation needs of workers and employers.
But Fuller charged UpSkill Houston and its stakeholders to do more, faster, and better, urging his audience to develop a very deliberate understanding of what it would take to re-train people with their spending power, financial resources, and discretionary time in mind.
“We cannot settle for incrementally better versions of what we’re doing,” he said.
Listen to the Managing the Future of Work podcast here. See images from the October 2019 UpSkill Works Future of Work Forum here. Learn more about UpSkill Houston here.
 The Houston Report
The Houston Report