Hydrogen Fuel Experiment to Take Off at IAH
Published May 23, 2024 by Taylor Tatum
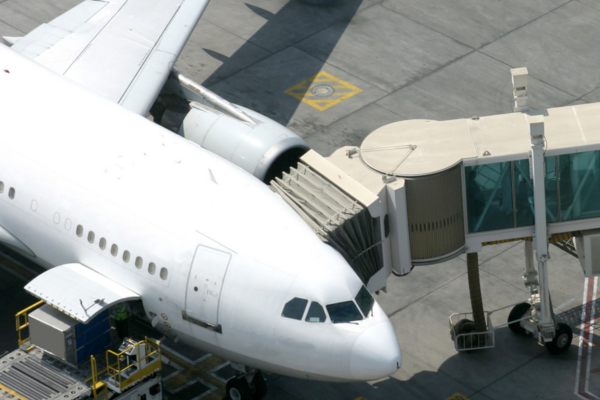
George Bush Intercontinental Airport (IAH) has been chosen as one of the five North American locations where Airbus will study the feasibility of creating a hydrogen hub.
The European multinational aerospace corporation is partnering with the Center for Houston’s Future (CHF) and Houston Airport System to examine the viability of equipping airports with the infrastructure to support hydrogen fuel for aircraft. The analysis, expected to conclude in March 2025, will focus on identifying potential opportunities and barriers to hydrogen usage at airports, as well as defining the requirements for an ‘end-to-end' hydrogen supply chain, as Airbus works to achieve its goal of having hydrogen commercial aircraft operational and carrying passengers by 2035.
“Building airplanes which run on clean hydrogen may take some time, but we can begin today by looking at how we can use clean hydrogen in airport operations, such as ground equipment and public transportation so we can be ready for the future,” CHF CEO Brett Perlman said.
The airline industry is increasingly investing in sustainable aviation fuel (SAF), an alternative fuel made from non-petroleum feedstocks that reduces emissions from air transportation to reach net zero carbon goals. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, aviation accounts for 2 percent of all carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions and 12 percent of all CO2 emissions from transportation worldwide. This collaborative effort can help accelerate SAF technology and adoption.
“As we continue to expand and modernize our facilities, participating in this sustainability study is crucial,” said Jim Szczesniak, Aviation Director for the City of Houston. “Continuing to build a sustainable airport system will ensure a healthy future for Houston, attract top talent and businesses, and demonstrate our commitment to being a responsible global citizen.”
The Airbus announcement follows the recent creation of the Sustainable Aviation Fuel Coalition, a nonprofit made up of key airlines, manufacturers and trade groups to advance the development of low-carbon fuels and decrease emissions in the industry. The organization will also advocate for federal policies that support the creation of a robust domestic market with lower prices and higher supply. Coalition members with a strong Houston presence include United Airlines, the Boeing Company and Sumitomo Corporation of Americas.
Other SAF developments include an agreement between United and Cemvita Corporation, a Houston-based cleantech startup focused on applying synthetic biology to enable a sustainable energy transition, to supply the airline with up to one billion gallons of sustainable aviation fuel from their first full-scale SAF plant over the next twenty years.
 The Houston Report
The Houston Report